Facial acne is a common skin disorder present in people of all age groups, especially in adolescents and early adulthood. Acne is one of the most common skin problems that is often associated with teenagers, but the truth is that there are also a lot of adults that are prone to acne due to its many causes. We hope this article will help you to learn everything about face acne: its causes and types, treatment modalities, as well as prevention strategies to get your skin health back!
What is Face Acne?
Face acne is a skin condition that develops when hair follicles become clogged with oil (sebum), dead skin cells, and bacteria. This blockage can cause different kinds of blemish like blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, and cysts. Understanding acne and treatment options that can help are critically important, since acne can have a major impact on self-esteem and mental health.
Types of Face Acne
Comedonal Acne: It includes blackheads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones). Blackheads are dark because the oil and dead skin that was trapped has reacted to oxygen, while whiteheads stay closed and look like little flesh-colored bumps.
Inflammatory Acne: Inflammatory acne includes red, swollen lesions and can be considered papules and pustules. Papules are small bumps that are usually tender, and pustules are similar but filled with pus.
Nodular Acne: Nodules are bigger, painful lumps that develop deep in the skin. If they were never treated, they can take some time to heal and can also leave scarring on the face.
Cystic Acne: This is the type of acne that is the most serious, with painful, pus-forming cysts that can lead to severe scarring. Cystic acne, on the other hand, is severe and needs to be treated.
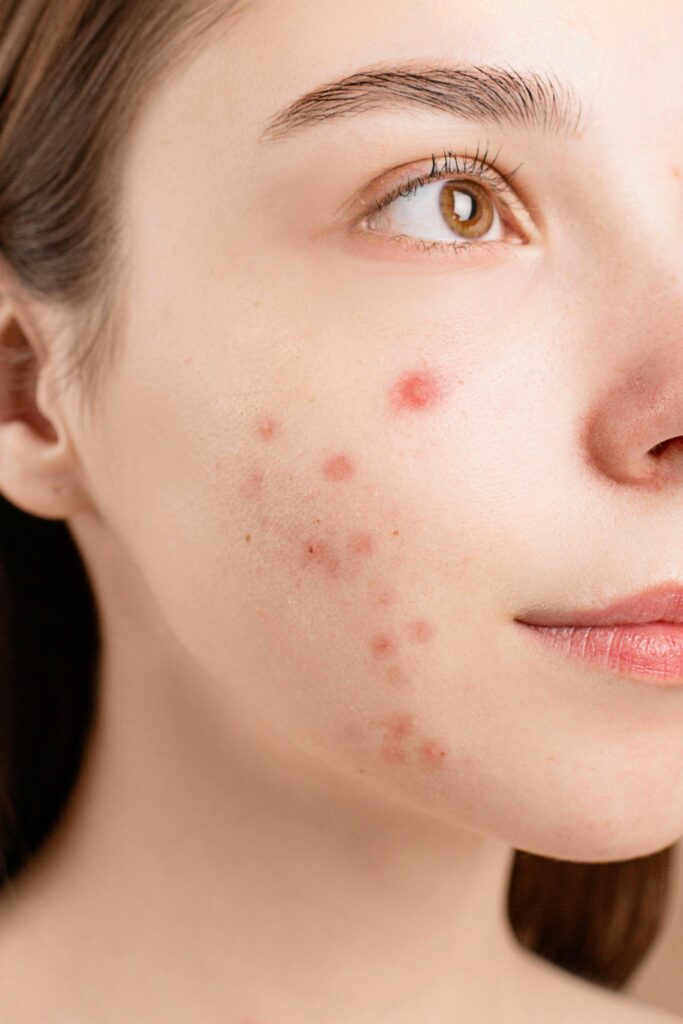

Causes of Face Acne
There are a number of reasons for face acne:
Hormonal fluctuations: Hormones are a major acne stimulator and androgen, especially, are elevated during puberty, menstruation and pregnancy. These hormones trigger sebaceous (oil) glands to make too much oil.
Bacteria: Our skin is home to many naturally occurring bacteria but overgrowth of Propionibacterium acnes can cause inflammation leading to acne breakouts.
Shedding Of Dead Skin Cells: Skin cells are constantly dying and being upstaged by new cells. These cells can build up in the pores and get stuck to sebum, life-determining blockages.
Diet: Some foods may cause a flare-up of acne. Some studies have suggested that diets high in sugar, dairy, and refined carbohydrates may trigger more acne.
Stress: Stress may increase the levels of cortisol, which can increase oil production and inflammation, worsening acne.
Triggers of Face Acne
Beyond the main drivers, environmental and lifestyle factors may provoke or aggravate breakouts:
Cosmetics: Weighty, oily make-up and skin care items are able to overload pores. Choose products that are non-comedogenic so they won’t aggravate breakouts.
If you are not cleansing your face regularly then there is a chance of the upper layer of your skin collecting dirt and oil and eventually resulting in acne.
Environmental factors: Air pollution, high humidity, and irritation of the skin by some chemicals can aggravate the skin and trigger acne.
Tight fitting clothing: Form-fitting hats or headbands for sweating can create a congested pore environment because they can hold bacteria and sweat against the skin and contribute to neck and forehead or temple breakout.
Diagnosis of Face Acne
Face acne may be diagnosed by a healthcare provider by examining your skin visually. They might inquire about your medical history, lifestyle, or any prior treatments you have attempted. In the case of severe or an unusual case of acne, more tests would be required to eliminate any underlying conditions.
How to Treat Face Acne
The type and severity of face acne determines what treatment will be effective. Here are some of the more common ones
Topical Treatments
Benzoyl peroxide — an over-the-counter treatment that attacks bacteria and minimizes inflammation. Available in multiple types, such as gels, creams, and cleansers.
Salicylic Acid: Salicylic acid, a well-known exfoliator, clears and opens pores while working against inflammation. Often used in cleansers, and spot treatments.
Retinoids: These vitamin A-derived products (examples include tretinoin and adapalene) prevent clogging of the pores and stimulate skin cell turnover. They can work for active acne and acne scars alike.
Topical Antibiotics — Clindamycin or erythromycin-based products meant to decrease bacteria on the skin and decrease inflammation.
Azelaic Acid — A natural acid that kills bacteria and reduces inflammation Use it for treating acne as well as rosacea.
Oral Medications
For more severe cases of face acne, your healthcare provider may prescribe oral medications:
Antibiotics: Doxycycline and minocycline are oral antibiotics that reduce bacteria and inflammation, which makes them effective at treating inflammatory acne.
Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin is a very potent oral retinoid that is usually prescribed for cystic acne that has failed other treatments. This medication has a lot of side effects and must be monitored closely by your health care provider.
Hormonal Therapy: In case of hormonal acne, phase of some contraceptive might be prescribed to balance your hormones which will help in reduction of breakouts. Hormonal fluctuations could also benefit from a pill like spironolactone, for example.
Using Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Apart from medical treatments, some home remedies and lifestyle modifications may be helpful in managing acne:
Regular Skincare Routine: Maintain a consistent regimen of washing, moisturizing, and applying acne medications as prescribed.
Healthy Diet A balanced diet that includes many fruits, vegetables, whole grains and good proteins. Minimize eating foods that are high in sugar and high in dairy.
Drink a Lot of Water: Consuming adequate water can keep your skin moisturized, and may help to eliminate toxins out of your body.
Refrain From Touching Your Face: You put bacteria and oil on your skin from your hands, which will make acne worse Do not put your face in your hands.
Sun protection: Application of sunscreen (non-comedogenic) should be done every day as UV rays aggravate the condition by causing inflammation
Prevention of Face Acne
We can’t eliminate acne completely, but do these to reduce the chances of an acne breakout:
Cleansing: Clean your face with a gentle face wash twice a day to remove excess oil and impurities.
Use Non-Comedogenic Products: Select makeup and skincare products that are non-comedogenic so they do not clog the pores.
Exfoliate:Remove dead skin cells and keep pores from clogging by exfoliating your skin 1-2 times a week, but be careful not to overdo it which can irritate skin.
Control stress: Include routine exercises like yoga or meditation in your schedule to help you manage stress, which helps balance hormones.
When You Need to Consult a Professional
Acne that does not go away with topical treatment; that gives you chronic problems; or that severely impacts your self-esteem, self-image, and mental health is a cause to reach out to your physician or dermatologist. They can offer customized treatment options and support to help you manage your acne.